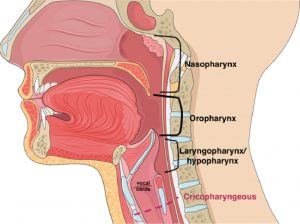
Standard oesophagus measures 18–26 cm in length. It can be divided into the cervical oesophagus ( pharyngoesophageal junction to the suprasternal notch) and the thoracic oesophagus, which continues to the diaphragmatic hiatus. There is a short portion known as abdominal oesophagus which measures only about 1.25 cm in length, lies on the posterior surface of the left lobe of the liver and only its front and left aspects are covered by peritoneum.
Upper and lower end points correspond to 6th cervical vertebra and 11th thoracic vertebra topographically, and the gastroesophageal junction usually correlates to xiphoid process of sternum.
When distended, the oesophageal lumen has internal dimensions of about 2 cm in the anteroposterior plane and 3 cm in the lateral plane. Solid food dysphagia becomes common when the lumen is narrowed to <13 mm (hence the aiming of balloon dilation of oesophageal stricture tends to be at least 10-13mm in diameter). Although this is variable and dysphagia can occur in larger lumen diameter when poorly masticated portions of food or at any diameter in motor disorders.
Endoscopically, the first narrow corresponds to upper oesophageal sphincter, at the level of the crycopharyngeous about 15cm from incisors and topographically corresponds to the corpus of the 6th cervical vertebra. The second narrow can be found at the crossing of aortic arch, at the level of the 4th thoracic vertebra topographically and measures 1.5–1.6 cm in width (23 cm after maxillary central incisor teeth, 7 cm below cricopharyngeal muscle)
The third classical narrowing forms at the crossing point of left main bronchium. This point is located at level of 5th dorsal vertebra, and 25-27 cm after maxillary central incisor teeth and 9 cm below oropharyngeal muscle. A fourth convex, pulsatile, extrinsic esophageal compression by left atrium can be found at 30cm, more pronounced in cases of Last narrowing is made by the right cruss of diagram at the osophageal hiatus, located at the level of 11th dorsal vertebra and 40 cm after maxillary central incisor teeth; it is 1–1.5 cm in length and1.5–1.8 cm in width, at the level of the lower esophageal sphincter.